Project
Quantification of Pulmonary Edema in Chest Radiographs
Heart failure is the leading cause of hospitalization in the US, with high readmission and mortality rates. Most of the acute heart failure patients present with pulmonary edema (fluid overload in their lungs) and exhibit heterogeneous responses to treatment for this fluid overload. This heterogeneity complicates effective treatment, which leads to long hospital stays and high readmission rates.
The treatment success in acute heart failure depends on effective management of patient fluid status, which in turn requires accurate monitoring of pulmonary edema. For example, a heart failure patient with a severe infection causing septic shock simultaneously needs both more fluid to optimize their hemodynamic function and less fluid to optimize their respiratory function. The accurate assessment of pulmonary edema is critical to maintaining this delicate fluid balance.
To support better clinical decision-making for heart failure patients and enable quantitative research on efficacy of treatments, We are developing machine learning algorithms to automatically and quantitatively assess the severity of pulmonary edema from chest x-ray images.
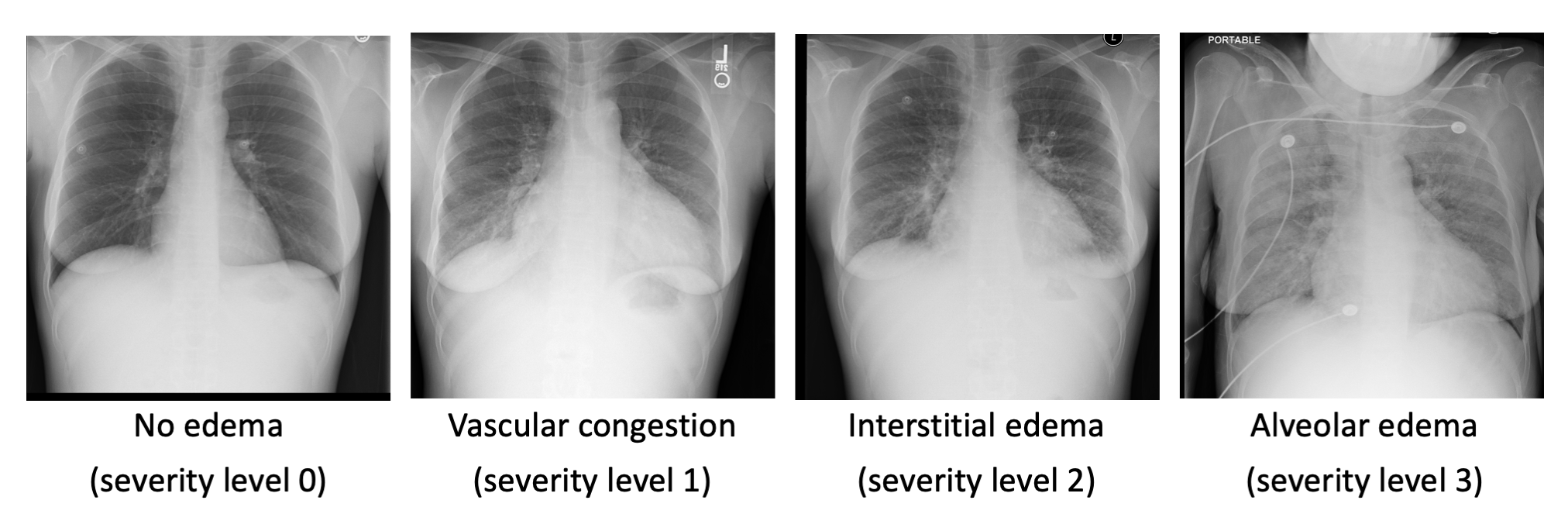
Representative chest x-ray images of pulmonary edema:
Contact us
If you would like to contact us about our work, please refer to our members below and reach out to one of the group leads directly.
Last updated Sep 23 '21



