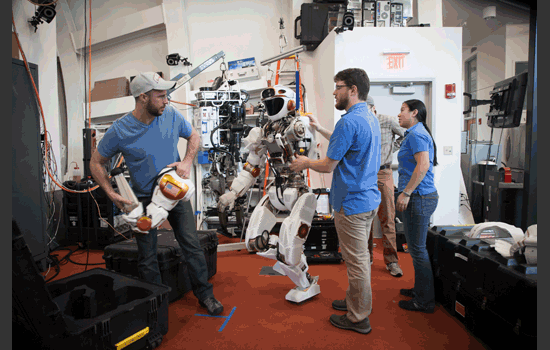
This week MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) received an unusual package: a six-foot-tall, 300-pound humanoid robot that NASA hopes to have serve on future space missions to Mars and beyond.
A team of researchers led by CSAIL principal investigator Russ Tedrake will program their new “Valkyrie” robot to autonomously perform a variety of challenging tasks that would allow it to help or even replace astronauts on missions.
Other researchers participating in the project include professors Leslie Kaelbling and Tomas Lozano-Perez, who will conduct work on high-level autonomy.
“Our work is about vetting the robot and seeing what it is capable of,” says Tedrake, whose team received a two-year research grant from NASA for the project. “If we can integrate the autonomy work with our planning and control algorithms, it could result in an unprecedented level of autonomous capabilities for a humanoid robot.’
Valkyrie is fully electric, with four body cameras, 28 torque-controlled joints, 44 degrees of freedom, and more than 200 individual sensors, including 38 on each hand (six on each palm, and eight along each of its four fingers).
Tedrake’s team at CSAIL’s Robot Locomotion Group has extensive experience developing autonomous robots. The group spent the last three years doing research as part of the DARPA Robotics Challenge, where they programmed another six-foot-tall robot named Atlas to complete a series of tasks that included opening doors, turning valves, drilling holes, climbing stairs and driving a car.
Besides the CSAIL team, NASA also awarded a Valkyrie robot to Northeastern University in conjunction with the University of Massachusetts at Lowell.